The Digital Solutions (DS) conducted an online Train-the-Trainers (TtT) program on the Enterprise Breeding System (EBS) from September 29 to October 17. The objective of the training was to provide extensive coaching to data managers from different CGIAR centers and partners on EBS features and capabilities, qualifying them to train end-users in their breeding programs.
Two batches of the two-week virtual sessions were held to accommodate participants from different time zones. Fourteen (14) participants attended from different crop breeding programs in the International Potato Center (CIP), the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT, the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA), and the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT).
The DS trainers introduced the EBS capabilities through tool demonstrations and hands-on exercises, and participants actively contributed to discussions on integrating them with their current breeding activities. The trainers also taught them topics on navigating the dashboard and tools, preparing experiments for field management and data collection, analyzing trials, and requesting genotyping services.
Additionally, the participants were trained on administrative capabilities in EBS, like creating new germplasm and inventory records, managing user access and organizational units, producing printouts, and overseeing genotype requests and data.
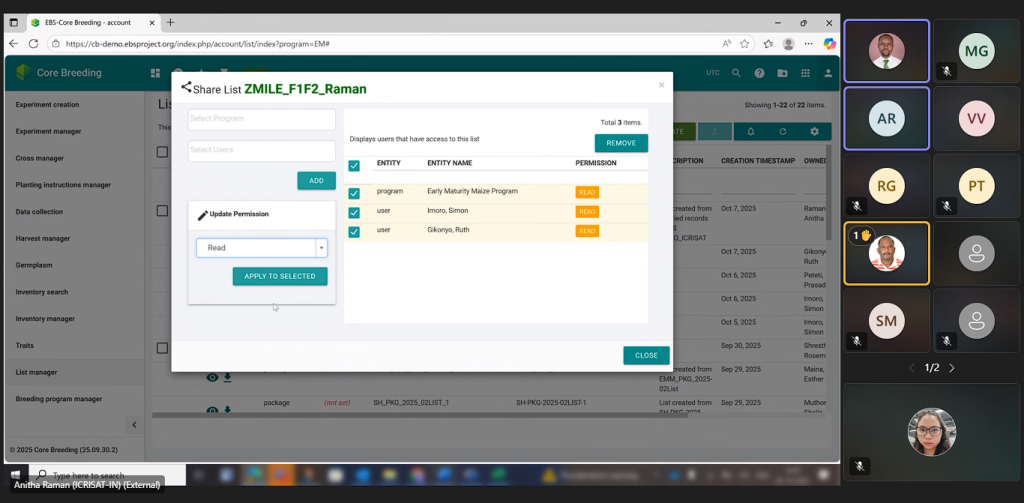
After the training sessions, the TtT participants exhibited their understanding of the EBS capabilities by replicating sample outputs and receiving constructive feedback from the trainers. They found the online training informative and helpful due to its clear delivery and practical examples. The participants also hoped for more sessions to deepen their understanding of certain features and capabilities.
As the CGIAR-preferred breeding data management system, customized EBS training sessions are conducted based on the requirements and contexts of current and prospective users. This ensures that adopting centers are ready to transform their crop breeding practices for faster breeding cycles and data-driven decisions.


